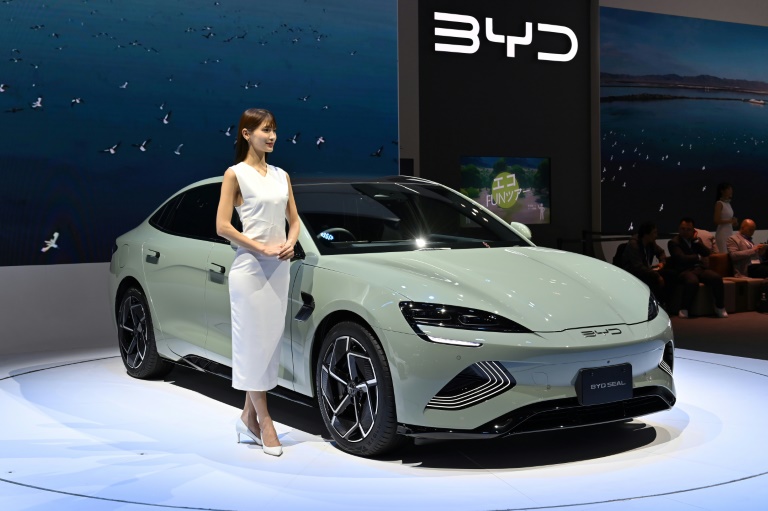
China’s BYD has overtaken US electric vehicle giant Tesla as the world’s leading EV deliverer, according to recent sales figures.
Here’s what you need to know about the Chinese electric vehicle firm with global ambitions.
Known as “Biyadi” in Chinese — or by the English slogan “Build Your Dreams” — BYD was founded in 1995 in the southern industrial hub of Shenzhen.
It initially specialised in the design and manufacture of batteries before moving into the automotive sector in 2003.
Close government cooperation in Shenzhen — where the public bus fleet has already fully transitioned to electric models — gave it an important boost.
“They were thinking about this way before any country was even considering trying to clean or electrify their public transportation fleets,” Tu Le, managing director of Sino Auto Insights, told AFP.
“I think that’s paid off currently with how competitive (BYD) are in the global passenger vehicle EV space.”
Last year BYD became the first manufacturer to pass the five million milestone in EV production, crowning itself “the world’s leading manufacturer of new energy vehicles”.
Many foreign automotive giants — including Tesla, BMW, Mercedes and Audi — depend on BYD for their batteries.
The firm has long benefited from generous subsidies from Beijing for electric vehicles — support that has angered other governments.
Beijing has spearheaded a targeted industrial strategy to boost its EV sector, pouring vast state funds into domestic firms as well as research and development.
As of the end of 2022, the Chinese government said it had spent more than 200 billion yuan ($28 billion) on subsidies and tax breaks for EV purchases alone.
The approach has given Chinese firms a critical edge in the race to provide cheaper, more fuel-efficient EVs over leading US automakers, which have not always enjoyed such state largesse.
Demand for electric vehicles has soared in recent years in China, which is the world’s biggest emitter of polluting greenhouse gasses.
BYD, whose investors include US investment titan Warren Buffet, wants electric and hybrid vehicles to lead its sales by 2035.
That push saw it announce sales of 526,409 all-electric cars in the fourth quarter of 2023 — surpassing Tesla’s 484,507 in the same period.
That has been helped by the fact BYD’s electric vehicles are cheaper, with its cars selling for less than $30,000 on average, while Tesla’s go for north of $40,000, according to financial magazine Barron’s.
It also sold more than 400,000 plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in the fourth quarter.
But despite its dominant position in the Chinese market, a number of growing domestic brands, including XPeng, Nio and Geely, are nipping at its heels.
XPeng said a total of 141,601 vehicles were delivered in 2023, while Nio reached 160,038 — both up from the year before.
Under intense pressure to outdo each other, China’s automakers are engaging in a price war, especially with consumer spending slowing as the country’s post-pandemic recovery stutters.
BYD ceased production of gasoline-powered vehicles last year and now focuses exclusively on hybrid and electric models.
It launched a European offensive in 2022 at the Paris Motor Show.
Last month, it said it would build a new EV plant in Hungary — in a move described by the country’s foreign minister as “one of the largest investments in the history of the Hungarian economy”.
That builds on its existing operations in the central European nation, including an electric bus factory.
It has said it hopes the factory will “accelerate the entry of new energy passenger vehicles into the European market” as well as deepen its global footprint.
But not everyone is happy with BYD’s westward expansion.
Last year, the European Union launched an investigation into Chinese subsidies for its EV sector, saying that Chinese state support has squeezed its own firms in local markets and threatening to impose tariffs in retaliation.