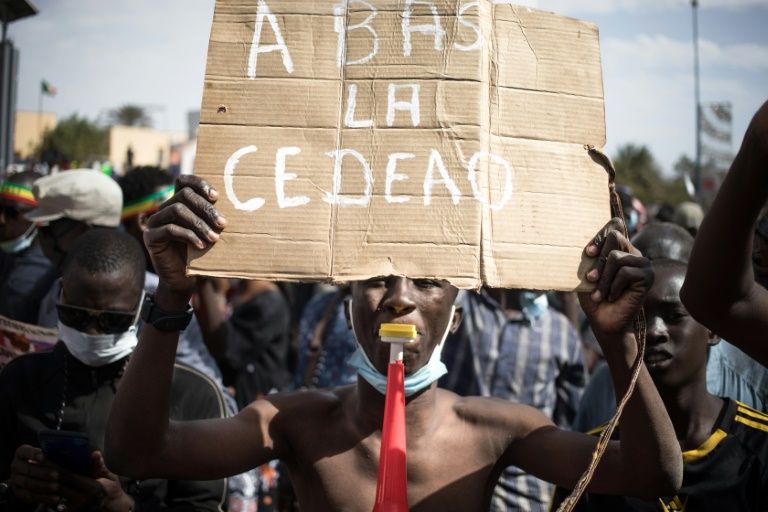[ad_1]
The military regimes in Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger announced Sunday their immediate withdrawal from the West African bloc ECOWAS, saying it has become a threat to member states.
The leaders of the three Sahel nations issued a statement saying it was a “sovereign decision” to leave the Economic Community of West African States “without delay”.
Struggling with jihadist violence and poverty, the regimes have had tense ties with ECOWAS since coups took place in Niger last July, Burkina Faso in 2022 and Mali in 2020.
All three — founding members of the bloc in 1975 — were suspended from ECOWAS with Niger and Mali facing heavy sanctions as the bloc tried to push for the early return of civilian governments with elections.
The sanctions were an “irrational and unacceptable posture” at a time when the three “have decided to take their destiny in hand” — a reference to the coups that removed civilian administrations.
The three nations have hardened their positions in recent months and joined forces in an “Alliance of Sahel States”.
The leaders’ joint statement added that 15-member ECOWAS, “under the influence of foreign powers, betraying its founding principles, has become a threat to member states and peoples”.
They accused the grouping of failing to help them tackle the jihadists who swept into Mali from 2012 and then on to Burkina and Niger.
Under pressure from the military regimes, France has removed ambassadors and troops and watched Russia fill the void militarily and politically.
The French army’s withdrawal from the Sahel — the region along the Sahara desert across Africa — has heightened concerns over the conflicts spreading southward to Gulf of Guinea states Ghana, Togo, Benin and Ivory Coast.
The prime minister appointed by Niger’s regime on Thursday blasted ECOWAS for “bad faith” after the bloc largely shunned a planned meeting in Niamey.
Niger had hoped for an opportunity to talk through differences with fellow states of ECOWAS which has has cold-shouldered Niamey, imposing heavy economic and financial sanctions following the military coup that overthrew elected president Mohamed Bazoum.
Niger’s military leaders, wrestling with high food prices and a scarcity of medicines, have said they want up to three years for a transition back to civilian rule.
In Mali, the ruling officers under Colonel Assimi Goita had pledged to hold elections in February this year, but that has now been pushed back to an unknown date.
Burkina Faso, which has not been put under sanctions although Captain Ibrahim Traore seized power in September 2022, has set elections for this summer, but says the fight against the insurgents remains the top priority.
[ad_2]
Source link